How Do I Upload Csv to Firestore
If you lot desire to migrate your existing database to Firestore, you might be wondering… How practise I import JSON or CSV to Firestore?. In this lesson, I will provide you with a reliable pipeline for reading raw data and parsing information technology to a writable format for Firestore.
Everybody has different data modeling needs, so I will teach y'all how to quickly roll out your ain NodeJS CSV-to-Firestore command line import tool. Its purpose is to take your local files (CSV or JSON format in this case), parse it to an array of JS objects, then use the Firebase admin SDK to perform an atomic batched write. Not only will this handle migrations, just information technology will likewise give y'all a solid development utility that you lot tin can extend with boosted functionality.
CSV format was called for this demo because it is usually used as an export format for relational SQL databases and MS Excel spreadsheets. If you want the opposite, scout episode 69 to larn how to [export Firestore to CSV](https://angularfirebase.com/lessons/csv-exports-from-firestore-database-with-cloud-functions/).
Source lawmaking bachelor to pro members. Learn more than
Full source lawmaking for the [Firestore migrator CLI tool](https://github.com/codediodeio/firestore-migrator).
Step 1 - Initial Setup
Let's get ahead and create an empty folder and initialized NPM.
mkdir firestore-importer cd firestore-importer npm init Setting upwardly a NodeJS TypeScript Projection
Yous can write this utility in vanilla JS, only TypeScript will dramatically ameliorate tooling and productivity long-term.
npm install -D typescript npm install -D @types/node touch on tsconfig.json mkdir src touch src/index.ts Now update your tsconfig.json with the following content. Basically, we're just telling TS to compile our code in the /dist folder as commonjs that can exist understood by NodeJS.
{ "compilerOptions" : { "outDir" : "./dist/" , "noImplicitAny" : imitation , "module" : "commonjs" , "target" : "es5" , "allowJs" : true , "sourceMap" : true , "moduleResolution" : "node" , "lib" : [ "es2015" ], "types" : [ "node" ] }, "include" : [ "src/**/*" ] } At this point, you can run tsc from the control line to compile your code.
Install the Firebase Admin SDK
npm install firebase-admin --save Y'all will need to download your service business relationship from the Firebase admin console. Save information technology in the root of this project and proper noun it credentials.json. This will give your local app full access to the project and bypass all security rules.
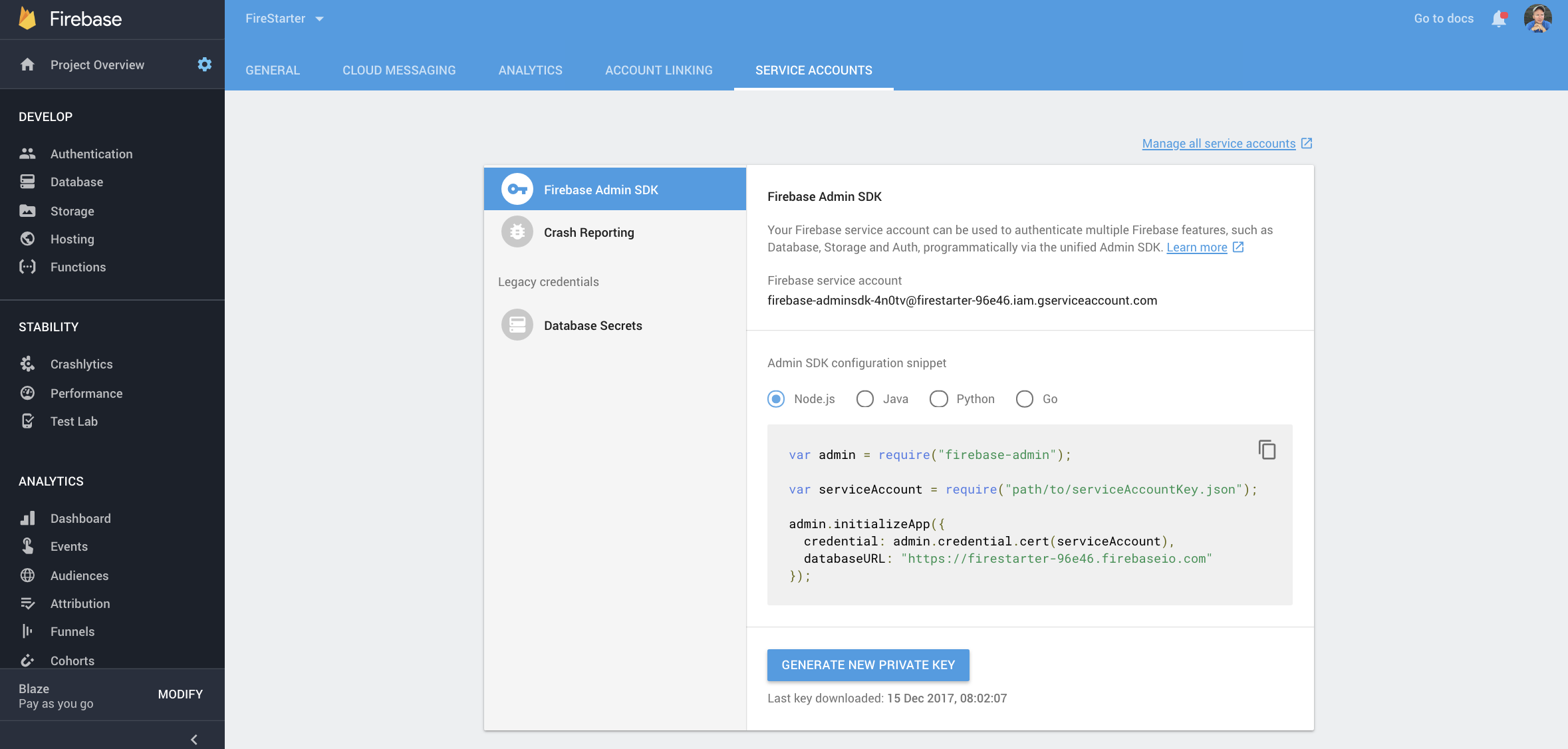
Firebase service account
Make sure to go on your credentials private. If using git, add the line `credentials.json` to your *.gitignore* file.
Install Commander
Commander.js is a tool that makes information technology piece of cake to parse command line arguments in Node. We will apply it to laissez passer a local file path and Firestore collection path argument to the migration command.
npm install commander --save Install FS Extra and CSVtoJSON
Lastly, allow's install FS Actress to collaborate with the local file organization. When information technology comes to CSV, there are a bunch of dissimilar Node packages, but CSVtoJSON works especially well for this task because it has a callback that emits each row from the spreadsheet as JSON.
npm i --save csvtojson fs-extra npm i -D @types/{csvtojson,fs-extra} The last initialization logic should wait something similar this.
# ! /usr/bin/env node import * every bit admin from 'firebase-admin' ; import * as fs from 'fs-actress' ; import * every bit args from 'commander' ; import * as csv from 'csvtojson' ; var serviceAccount = require ( "../credentials.json" ); admin . initializeApp ({ credential: admin.credential.cert ( serviceAccount ) }); const db = admin . firestore (); Pace 2 - Parsing Raw Data
Our adjacent pace is to read a raw file, then convert it to a JavaScript object that can be used every bit the document data in Firestore.
Reading a JSON File
Reading a raw JSON file is an piece of cake 1-liner thanks to fs-extra.
fs . readJSON ( 'hullo.json' ); CSV to JSON
Reading a CSV is a bit more than work. CSVtoJSON uses callbacks, but we will Promisify information technology in the next department. It gives us a scattering of listeners that emit information when a row or document is finished processing.
csv () . fromFile ( path ) . on ( 'json' , ( row ) => { // emits each row }) . on ( 'end_parsed' , ( data ) => { // emits all rows }) . on ( 'error' , err => { // handle errors }) }) While it's possible to process command line arguments in Node without any dependencies, I highly recommend the Commander.js package to make life easier for your team.
Hither'due south how we want our CLI command to piece of work:
burn-drift --src bunnies.csv --collection animals It should read the CSV source file, then write each row as a document in Firestore. Accessing arguments from the command is every bit simple as defining them as an options.
args . version ( '0.0.1' ) . option ( '-s, --src <path>' , 'Source file path' ) . pick ( '-c, --collection <path>' , 'Collection path in database' ) . selection ( '-i, --id [id]' , 'Optional field to employ for document ID' ) . parse ( process . argv ); // At present use the args in your script const file = args . src ; const colPath = args . drove ; As an added bonus, we go instant documentation for the CLI tool.
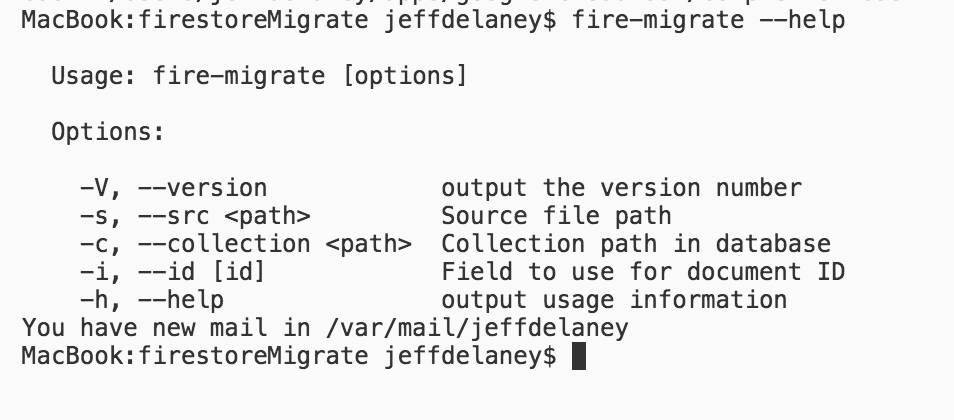
CLI output
Full Firebase CLI Code
Now information technology's time to put everything together into a CLI tool that nosotros can actually use.
# ! /usr/bin/env node import * as admin from "firebase-admin" ; import * as csv from "csvtojson" ; import * as fs from "fs-actress" ; import * as args from "commander" ; args . version ( "0.0.1" ) . option ( "-s, --src <path>" , "Source file path" ) . option ( "-c, --collection <path>" , "Collection path in database" ) . choice ( "-i, --id [id]" , "Field to employ for document ID" ) . parse ( process . argv ); // Firebase App Initialization var serviceAccount = require ( "../credentials.json" ); admin . initializeApp ({ credential: admin.credential.cert ( serviceAccount ) }); const db = admin . firestore (); // Chief migration function async part migrate() { attempt { const colPath = args . drove ; const file = args . src ; // Create a batch to run an diminutive write const colRef = db . collection ( colPath ); const batch = db . batch (); let data ; if ( file . includes ( ".json" )) { data = expect fs . readJSON ( file ); } if ( file . includes ( ".csv" )) { data = await readCSV ( file ); } for ( const detail of data ) { const id = args . id ? item [ args . id ]. toString () : colRef . doctor (). id ; const docRef = colRef . doc ( id ); batch . set ( docRef , particular ); } // Commit the batch await batch . commit (); panel . log ( "Firestore updated. Migration was a success!" ); } catch ( error ) { console . log ( "Migration failed!" , error ); } } part readCSV ( path ) : Promise < any > { render new Promise (( resolve , refuse ) => { let lineCount = 0 ; csv () . fromFile ( path ) . on ( "json" , information => { // fired on every row read lineCount ++ ; }) . on ( "end_parsed" , data => { console . info ( `CSV read complete. ${ lineCount } rows parsed.` ); resolve ( information ); }) . on ( "error" , err => refuse ( err )); }); } // Run migrate (); Compile the Code and Link the Command
To connect our Node executable file to the local command line PATH, we need to register it in the bin object in bundle.json.
"bin" : { "fire-drift" : "dist/index.js" } You can compile the source code and link the command past running:
The Cease
Every bit you can see, creating your own CLI tool for Firebase development is pretty uncomplicated. You can expand on this code to build additional utilities that increment your development productivity.
Source: https://fireship.io/lessons/import-csv-json-or-excel-to-firestore/
0 Response to "How Do I Upload Csv to Firestore"
Post a Comment